ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) in the Telecommunications Sector
- Analyst Interview
- Nov 3, 2024
- 9 min read
Understanding ARPU in Telecommunications
ARPU, or Average Revenue Per User, is a straightforward yet powerful indicator for businesses, particularly in subscription-based sectors like telecommunications. ARPU reveals how much revenue a telecom provider generates, on average, from each active user. While telecom operators have a range of key performance indicators (KPIs) to track, ARPU serves as a top metric since it reflects both user engagement levels and the effectiveness of pricing strategies.
Unlike metrics focused on subscriber count or growth alone, ARPU provides a clear picture of the revenue derived from an existing customer base, helping to highlight revenue consistency and stability. This insight is critical because, in competitive markets, maintaining or growing ARPU often translates to enhanced profitability and value creation without requiring continuous expansion in user numbers.

Why ARPU is Essential in the Telecommunications Industry
ARPU plays a central role in the financial health of telecommunications companies. Here’s why it matters:
Profitability Indicator: High ARPU typically correlates with better profitability as it reflects greater spending per customer. Telecom companies use this to gauge the revenue efficiency of their customer base.
Customer Value Insights: By segmenting customers according to ARPU, telecom providers can identify high-value users and tailor premium services to retain them.
Revenue Forecasting and Budgeting: Tracking ARPU allows operators to project future revenue with greater accuracy, especially when used alongside other metrics like churn rate or net adds.
Strategic Planning: ARPU trends help telecom operators determine how much to invest in network expansion, technology upgrades, or customer acquisition strategies based on revenue potential.
As a reliable measure of revenue derived from each subscriber, ARPU effectively answers a critical question: how valuable is each customer?
Calculating ARPU in Telecommunications
Calculating ARPU is straightforward yet requires a few specific inputs. The formula generally used in telecommunications is as follows:

In telecom, total revenue often includes fees from voice, data, and messaging services, as well as any additional charges for value-added services (VAS) or international roaming.
Examples of ARPU Calculations
1. AT&T Inc.
AT&T, a major telecom player in the U.S., reports ARPU figures for its wireless segment, often differentiated between postpaid (long-term subscribers) and prepaid (pay-as-you-go subscribers).
Calculation Example

So, AT&T's quarterly ARPU for postpaid subscribers would be approximately $266.67.
Explanation
A higher ARPU for postpaid services indicates that AT&T’s subscribers are utilizing premium services or subscribing to high-tier data plans. This quarterly figure can be broken down to a monthly ARPU of about $89, which aligns with AT&T’s focus on postpaid subscribers who generally spend more than prepaid customers.
2. Verizon Communications Inc.
Verizon, another major U.S. telecom provider, frequently reports wireless postpaid ARPU, especially for individual smartphone users, since this group is a key revenue driver.
Calculation Example

Thus, Verizon's quarterly ARPU is approximately $275.
Explanation
Verizon's strong ARPU for smartphone users highlights its pricing power and the value it derives from bundled services, like premium data and 5G plans. This quarterly ARPU translates to about $91.67 per month, signaling a high-spending customer base in a competitive market.
3. T-Mobile US Inc.
T-Mobile's ARPU calculation includes both postpaid and prepaid customer revenue. The company often emphasizes postpaid ARPU, as postpaid subscribers are typically more consistent in revenue contribution.
Calculation Example

So, T-Mobile’s quarterly postpaid ARPU is $250.
Explanation
At a quarterly ARPU of $250 (or around $83.33 monthly), T-Mobile’s figure may appear lower compared to AT&T or Verizon. However, T-Mobile’s strategy often involves competitive pricing and plans that attract value-conscious customers, thus providing strong revenue from a broad base of users.
4. Vodafone Group Plc
Vodafone, a global telecom provider, reports ARPU across various regions, such as Europe and Africa, where it operates in both high-income and emerging markets. Here, we use Vodafone’s average ARPU for its European market.
Calculation Example

Vodafone’s quarterly ARPU in Europe is around $142.86.
Explanation
This ARPU indicates the diversity of Vodafone’s market, reflecting lower revenue per user than in the U.S. market. At approximately $47.62 per month, this figure shows the balance between Vodafone’s premium markets in Europe and its emerging-market strategy, where revenue per user is generally lower.
5. China Mobile Ltd.
China Mobile, the largest telecom operator in China, has a significant subscriber base and operates in a highly competitive, lower-ARPU environment. Their ARPU is calculated across millions of users in a value-driven market.
Calculation Example

Thus, China Mobile’s quarterly ARPU is approximately $36.84.
Explanation
China Mobile’s ARPU reflects a vast user base and a value-centric model, with an ARPU of about $12.28 monthly. This figure is typical in emerging markets, where high subscriber volumes compensate for lower per-user revenue, helping maintain revenue stability.
Key Components Influencing ARPU
Several factors shape ARPU in the telecommunications sector. Let’s look at the major components impacting it:
User Base and Segmentation
The size and demographics of the user base significantly influence ARPU. Telecom providers often segment their customer base into high, medium, and low-value tiers, allowing for more targeted service offerings. For example, high-value customers typically prefer premium services and are willing to pay for higher data speeds or exclusive features, which positively impacts ARPU.
Pricing and Service Bundling Strategies
Pricing strategies can directly affect ARPU. Telecom providers frequently use bundles that package data, voice, and messaging services to encourage higher spending. Promotional pricing and discounts can reduce ARPU temporarily, but bundled offerings generally increase customer commitment, thereby enhancing ARPU in the long run.
Data Consumption Patterns
The shift towards data-heavy services has revolutionized telecom ARPU. The increasing demand for streaming, gaming, and high-definition video conferencing has led to a marked rise in data consumption, driving up ARPU. With this in mind, telecom companies are expanding their data offerings and setting tiered data limits to maximize revenue per user.
Value-Added Services (VAS)
ARPU can also benefit from value-added services like music or video streaming, mobile wallets, and cloud storage, which supplement core offerings. These additional services not only diversify revenue streams but also deepen customer engagement with the platform, which can increase ARPU sustainably.
Trends Shaping ARPU in Telecommunications
As digital transformation sweeps across the industry, new trends are influencing ARPU in innovative ways. Key trends include:
Growth of 5G Networks
With the deployment of 5G, telecom companies are witnessing a renewed interest in premium data plans, which is positively affecting ARPU. As users upgrade to 5G for better speeds and lower latency, telecom providers have an opportunity to offer more data-intensive services, justifying higher charges and enhancing ARPU.
Convergence of Services
Telecommunications companies are increasingly offering converged services—combining mobile, broadband, and TV services under one umbrella. Known as “quad-play,” this approach bundles multiple services, which encourages higher spending per customer and reduces churn, subsequently increasing ARPU.
Digital Service Expansion
Telecom operators are investing in digital ecosystems, providing services like mobile payment systems, e-commerce platforms, and smart home solutions. These digital expansions help improve ARPU by creating new revenue streams and ensuring customers spend more time within the telecom provider’s offerings.
Usage-Based Pricing Models
As traditional fixed-fee models become less sustainable, usage-based pricing models have emerged as an alternative. These models allow customers to pay according to usage, with high-use customers generating more revenue. Usage-based pricing ensures that heavy data users contribute to a higher ARPU, supporting revenue growth for providers.
ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) vs Other Metrics
Let’s explore how ARPU compares to other key telecom metrics, their unique contributions, and how they complement each other in strategic decision-making.
ARPU vs. Total Revenue
Key Differences
ARPU focuses on the revenue contribution of each individual user, whereas Total Revenue captures the cumulative revenue from all sources and users over a specific period.
Formula for ARPU:
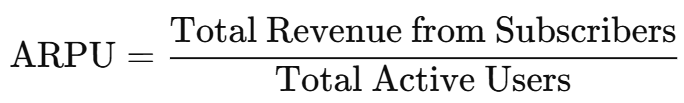
Formula for Total Revenue:
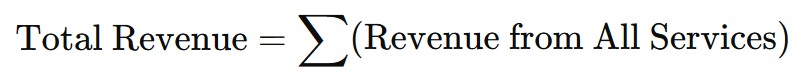
Complementary Insights
Total Revenue reflects the overall market reach, growth potential, and scale of the business, while ARPU provides insights into revenue efficiency per user. If a company’s total revenue grows without an increase in ARPU, it may indicate expansion through low-value users. Conversely, a stable or rising ARPU with modest revenue growth suggests effective monetization of existing users rather than aggressive market expansion.
Example Scenario
If a telecom company sees a $10 million increase in total revenue but a decline in ARPU, this might suggest aggressive acquisition of lower-spending customers, which could affect profitability long term.
ARPU vs. Churn Rate
Key Differences
ARPU measures average revenue per user, while Churn Rate calculates the percentage of subscribers who leave a service over a given period.
Formula for Churn Rate:

Complementary Insights
Churn Rate is critical for understanding customer retention, which directly impacts ARPU. High ARPU is more sustainable when churn is low, as retaining existing high-value users typically costs less than acquiring new ones. A rising churn rate with stable ARPU could indicate dissatisfaction among high-paying customers, which may ultimately harm profitability.
Example Scenario
A telecom provider with a high ARPU but also a high churn rate might be overspending on retaining users, reducing long-term profitability. Lowering churn through improved customer service could stabilize or even increase ARPU.
ARPU vs. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Key Differences
ARPU measures short-term revenue per user, while Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) estimates the total revenue a company can expect from a user over their entire relationship.
Formula for CLV

Complementary Insights
CLV provides a long-term view by integrating ARPU with churn rate and average customer lifespan. A high ARPU with low CLV suggests a short user lifecycle, indicating that customers are spending significantly but are not loyal over time. Telecoms can use this to adjust customer retention strategies or service offerings to enhance loyalty.
Example Scenario
If a telecom company’s ARPU is $50 but the CLV is only $200, customers may only stay for four months on average. Improving customer experience or loyalty programs could increase the CLV by extending the customer lifespan, thereby increasing overall profitability.
ARPU vs. Gross Margin
Key Differences
ARPU focuses on revenue per user, while Gross Margin measures profitability, calculated as the revenue minus the cost of goods or services sold, expressed as a percentage of revenue.
Formula for Gross Margin:

Complementary Insights
Gross Margin highlights the cost efficiency in delivering services, which, when combined with ARPU, reveals whether high ARPU is translating into profitable growth. A high ARPU with a low gross margin suggests high service costs, possibly from expensive customer acquisition or network costs. Improving efficiency without reducing ARPU can significantly impact profitability.
Example Scenario
A telecom company with an ARPU of $80 but a gross margin of only 20% may be facing high operational costs. Reducing these costs, perhaps by shifting to more efficient digital services, could improve gross margin without impacting ARPU.
ARPU vs. Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)
Key Differences
ARPU measures revenue per user, while Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA) measures revenue per customer account. Multiple users or lines can exist under one account (e.g., family plans), which makes ARPA a more aggregate measure.
Formula for ARPA:

Complementary Insights
While ARPU reflects revenue per individual user, ARPA can provide insights into account-level revenue, especially useful for telecom providers offering family or corporate plans. High ARPA often indicates that accounts have multiple users or services, while low ARPU suggests individual users are not heavily monetized. This comparison helps telecoms decide if they should prioritize single-user or multi-user account growth.
Example Scenario
A telecom provider with a low ARPU but a high ARPA might focus on family plans that bring in more users per account. This strategy can increase customer loyalty, as multiple users under one account are less likely to churn than individual users.
ARPU vs. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Key Differences
ARPU measures revenue generation, while Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures customer satisfaction and likelihood to recommend the service.
Formula for NPS:

Complementary Insights
NPS indicates customer sentiment, which, when cross-referenced with ARPU, reveals if high-spending customers are also satisfied customers. If high ARPU corresponds with a low NPS, it may mean customers feel the service isn’t worth the cost, increasing the risk of churn. Improving customer satisfaction could stabilize or even increase ARPU by encouraging positive word-of-mouth and customer retention.
Example Scenario
A telecom company with a high ARPU of $70 but an NPS of 20 might have room to improve service quality or customer experience. Boosting NPS can lead to a positive cycle where satisfied customers are willing to spend more and stay longer, increasing both ARPU and customer loyalty.
FAQs
What is ARPU in telecommunications?
ARPU, or Average Revenue Per User, is a measure of revenue generated per subscriber, indicating the average earnings from each active user over a specified period.
Why is ARPU important?
ARPU is crucial as it provides insights into customer revenue contribution, pricing effectiveness, and helps forecast revenue potential, aiding strategic decisions.
How is ARPU calculated in telecom?
ARPU is calculated by dividing the total revenue generated by the number of active users within a specific timeframe.
What factors impact ARPU?
Key factors include data consumption, service pricing, add-on services, and the number of active users.
How can telecom companies increase ARPU?
Companies can increase ARPU by offering premium plans, promoting data-heavy applications, and adding value-added services like streaming and mobile wallets.
What challenges do telecoms face in boosting ARPU?
Challenges include market saturation, intense competition, and high infrastructure costs, which can pressure pricing and reduce ARPU.
-min.png)
-min.png)
Comments